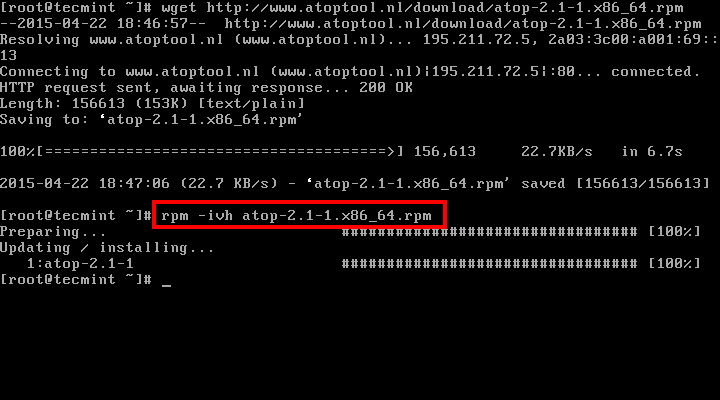
Install Packages With Rpm
4.14.0 / 12 October 2017; 2 months ago ( 2017-10-12) Written in, Website RPM Package Manager ( RPM) (originally Red Hat Package Manager; now a ) is a. The name RPM refers to the following: the.rpm, files in the.rpm file format, packaged in such files, and the package manager program itself.
RPM was intended primarily for; the file format is the baseline package format of the. Even though it was created for use in, RPM is now used in many. It has also been ported to some other, such as (as of version 6.5 SP3) and (as of version 4). An RPM package can contain an arbitrary set of files.
How to Install or Remove an RPM Package Method 1 Installation. Download your desired RPM package. Method 2 Removal. Open a terminal window, and type: rpm -e.packagename. Method 3 rpm codes. The rpm -i command syntax is listed below.
The larger part of RPM files encountered are “binary RPMs” (or BRPMs) containing the compiled version of some software. There are also “source RPMs” (or SRPMs) files containing the used to produce a package. These have an appropriate tag in the file header that distinguishes them from normal (B)RPMs, causing them to be extracted to /usr/src on installation. SRPMs customarily carry the file extension “.src.rpm” (.spm on file systems limited to 3 extension characters, e.g. Contents. History RPM was originally written in 1997 by Erik Troan and Marc Ewing, based on pms, rpp, and pm experiences.
Pm was written by Rik Faith and Doug Hoffman in May 1995 for Red Hat Software, its design and implementations influenced greatly by pms, a package management system by Faith and Kevin Martin in the fall of 1993 for the Bogus Linux Distribution. Pm preserves the ' + patches' paradigm of pms, while adding features and eliminating arbitrary limitations present in the implementation. Pm provides greatly enhanced database support for tracking and verifying installed packages Features For a performing software installation and maintenance, the use of package management rather than manual building has advantages such as simplicity, consistency and the ability for these processes to be automated and non-interactive. Features of RPM include:. RPM packages can be cryptographically verified with and.
Original source archive(s) (e.g.tar.gz,.tar.bz2) are included in SRPMs, making verification easier. PatchRPMs and DeltaRPMs, the RPM equivalent of a file, can incrementally update RPM-installed software. Automatic build-time dependency evaluation. Local operations Packages may come from within a particular distribution (for example ) or be built for it by other parties (for example for Fedora). Circular dependencies among mutually dependent RPMs (so-called ') can be problematic; in such cases a single installation command needs to specify all the relevant packages. Repositories RPMs are often collected centrally in one or more on the internet. A site often has its own RPM repositories which may either act as local mirrors of such internet repositories or be locally maintained collections of useful RPMs.
Front ends Several to RPM ease the process of obtaining and installing RPMs from repositories and help in resolving their dependencies. These include:. used in, 5, 5 and above, and., introduced in 18, default since. used in, 3 and 4, and. used in, and.

used in, and., a port of Debian's (APT) used in, and., used in Unity Linux, available for many distributions including. rpmquery, a command-line utility available in (for example) Red Hat Enterprise Linux Local RPM installation database Working behind the scenes of the package manager is the RPM database, stored in /var/lib/rpm. It uses as its back-end. It consists of a single database ( Packages) containing all of the meta information of the installed rpms. Multiple databases are created for indexing purposes, replicating data to speed up queries. The database is used to keep track of all files that are changed and created when a user (using RPM) installs a package, thus enabling the user (via RPM) to reverse the changes and remove the package later.
If the database gets corrupted (which is possible if the RPM client is ), the index databases can be recreated with the rpm -rebuilddb command. Description Whilst the RPM format is the same across different, the detailed conventions and guidelines may vary across them.
Package filename and label An RPM is delivered in a single file, normally in the format: -.rpm such as: libgnomeuimm-2.0-2.0.0-3.i386.rpm where is libgnomeuimm, is 2.0, is 2.0.0-3, and is i386. Source code may also be distributed in RPM packages in which case the part is specified as src as in, libgnomeuimm-2.0-2.0.0-3. Src.rpm RPMs with the noarch.rpm extension refer to packages which do not depend on a certain computer's architecture. These include graphics and text for another program to use, and programs written in interpreted programming languages such as programs and.
The RPM contents also include a package label, which contains the following pieces of information:. software name.
software version (the version taken from original source of the software). package release (the number of times the package has been rebuilt using the same version of the software). This field is also often used for indicating the specific distribution the package is intended for by appending strings like 'mdv' (formerly, 'mdk') , 'mga' , 'fc4' ( 4), 'rhl9' (Red Hat Linux 9), 'suse100' ( 10.0) etc.
architecture for which the package was built (i386, i686, x8664, ppc, etc.) The package label fields do not need to match the filename. Library packaging Libraries are distributed in two separate packages for each version. One contains the precompiled code for use at run-time, while the second one contains the related development files such as headers, etc. Those packages have '-devel' appended to their name field. The system administrator should ensure that the versions of the binary and development packages match.
Format The format is binary and consists of four sections:. The lead, which identifies the file as an RPM file and contains some obsolete headers. The signature, which can be used to ensure integrity and/or authenticity. The header, which contains including package name, version, architecture, file list, etc. A file archive (the ), which usually is in format, compressed with.
The rpm2cpio tool enables retrieval of the cpio file without needing to install the RPM package. More recent versions of RPM can also use, or compression. RPM 5.0 format supports using for archiving. SPEC file The 'Recipe' for creating an RPM package is a spec file. Spec files end in the '.spec' suffix and contain the package name, version, RPM revision number, steps to build, install, and clean a package, and a changelog. Multiple packages can be built from a single RPM spec file, if desired.
Currently LEGO Star Wars The Force Awakens licence serial keygen is tested for PS4 / Xbox one console/MAC/Vista/ Windows 7 / Windows8 and Win 10. LEGO Star Wars The Force Awakens keygen tester results are good on lower versions of windows as well. We have made the application very simple. Strictly follow the guide for the successful download of Lego Star Wars The Force Awakens Redeem Code Generator and the game.You must be thinking to get lego star wars the force awakens Xbox one iso,ps4 iso,xbox 360 iso,ps3 iso from the kickass torrent and the piratebay torrent.But i warn you that. Lego Star Wars: The Force Awakens Keygen is a free app for generating Lego Star Wars: The Force Awakens activation code, serial key and redeem code. This Keygen is easy to use tool that even a five years old kid can generate keys using this tool. By using Lego Star Wars: The Force Awakens Key Generator you can. Home Tags LEGO STAR WARS The Force Awakens activation key. Tag: LEGO STAR WARS The Force Awakens activation key. LEGO STAR WARS THE FORCE AWAKENS Torrent Pc LEGO STAR WARS THE FORCE AWAKENS LEGO STAR WARS The Force Awakens XBOX 360 Download. LEGO STAR WARS The. Issuu is a digital publishing platform that makes it simple to publish magazines, catalogs, newspapers, books, and more online. Easily share your publications and get them in front of Issuu's millions of monthly readers. Title: LEGO Star Wars The Force Awakens Product Key, Author: plumjade216, Name:. Lego star wars force awakens.
RPM packages are created from RPM spec files using the rpmbuild tool. Spec files are usually distributed within SRPM files, which contain the spec file packaged along with the source code. SRPM A typical RPM is pre-compiled software ready for direct installation. The corresponding source code can also be distributed. This is done in an SRPM, which also includes the 'SPEC' file describing the software and how it is built. The SRPM also allows the user to compile, and perhaps modify, the code itself. A software package may contain only scripts that are architecture-independent.
In such a case only an SRPM may be available; this is still an installable RPM. Forks As of June 2010, there are two versions of RPM in development: one led by the Fedora Project and Red Hat, and the other by a separate group led by a previous of RPM, a former employee of Red Hat. RPM.org The rpm.org community's first major code revision was in July 2007; version 4.8 was released in January 2010, version 4.9 in March 2011, 4.10 in May 2012, 4.11 in January 2013, 4.12 in September 2014 and 4.13 in July 2015. This version is used by distributions such as, and, and formerly (until 2010).
RPM v5 Jeff Johnson, the RPM maintainer since 1999, continued development efforts together with participants from several other distributions. RPM version 5 was released in May 2007. This version is used by distributions such as (until Wind River Linux 10), Rosa Linux, and (former which switched to rpm5 in 2011 ) and also by the project which provides packages for other common UNIX-platforms. OpenMandriva Lx considered switching back to rpm.org before folding. Switched back to rpm.org due to issues in RPM5. See also.

Retrieved 2011-12-11. Retrieved 2011-01-20. Archived from on 2016-11-05.
Retrieved 2013-08-25. ^ Bailey, Edward C. 'Chapter 1: An Introduction to Package Management'. Red Hat, Inc.
Archived from on 2016-09-10. Retrieved 2013-08-13. ^ Bailey, Edward C. 'Appendix A: Format of the RPM File'.
Red Hat, Inc. Archived from on 2016-04-21. Retrieved 2010-11-22. Retrieved 2014-04-14.
Retrieved 2014-04-14. Retrieved 2010-11-22. USENIX Association. Retrieved 2011-03-15.
Archived from on 2013-09-25. Retrieved 2014-04-14. Ark Linux Official Site.
Archived from on 2012-02-11. Retrieved 2014-04-14. Retrieved 2011-11-11. Fedora Project.
Redhat Install Packages With Rpm
Retrieved 2011-11-11. Archived from on 2016-03-04. Retrieved 2013-10-24. Retrieved 2014-04-14. Bodnar, Ladislav & Smith, Jesse (2010-11-22). Retrieved 2010-11-22. Retrieved 2017-04-19.
Retrieved 2017-12-04. External links. by Matt Frye in.